language
Unlocking Precision: The Art of Welding Techniques for Industrial Applications
Dec 07,2025
Unlocking Precision: The Art of Welding Techniques for Industrial Applications
Table of Contents
Introduction to Industrial Welding Techniques
The Importance of Precision in Welding
Overview of Popular Welding Methods
Arc Welding Techniques
MIG Welding: A Versatile Choice
TIG Welding: Achieving High Precision
Unlocking Precision: The Art of Welding Techniques for Industrial Applications
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Industrial Welding Techniques
- The Importance of Precision in Welding
- Overview of Popular Welding Methods
- Arc Welding Techniques
- MIG Welding: A Versatile Choice
- TIG Welding: Achieving High Precision
- Spot Welding: Fast and Efficient
- Choosing the Right Welding Technique for Your Application
- Essential Welding Equipment and Components
- Advanced Techniques for Enhanced Precision
- Safety Practices in Industrial Welding
- The Future of Welding Technologies
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Welding
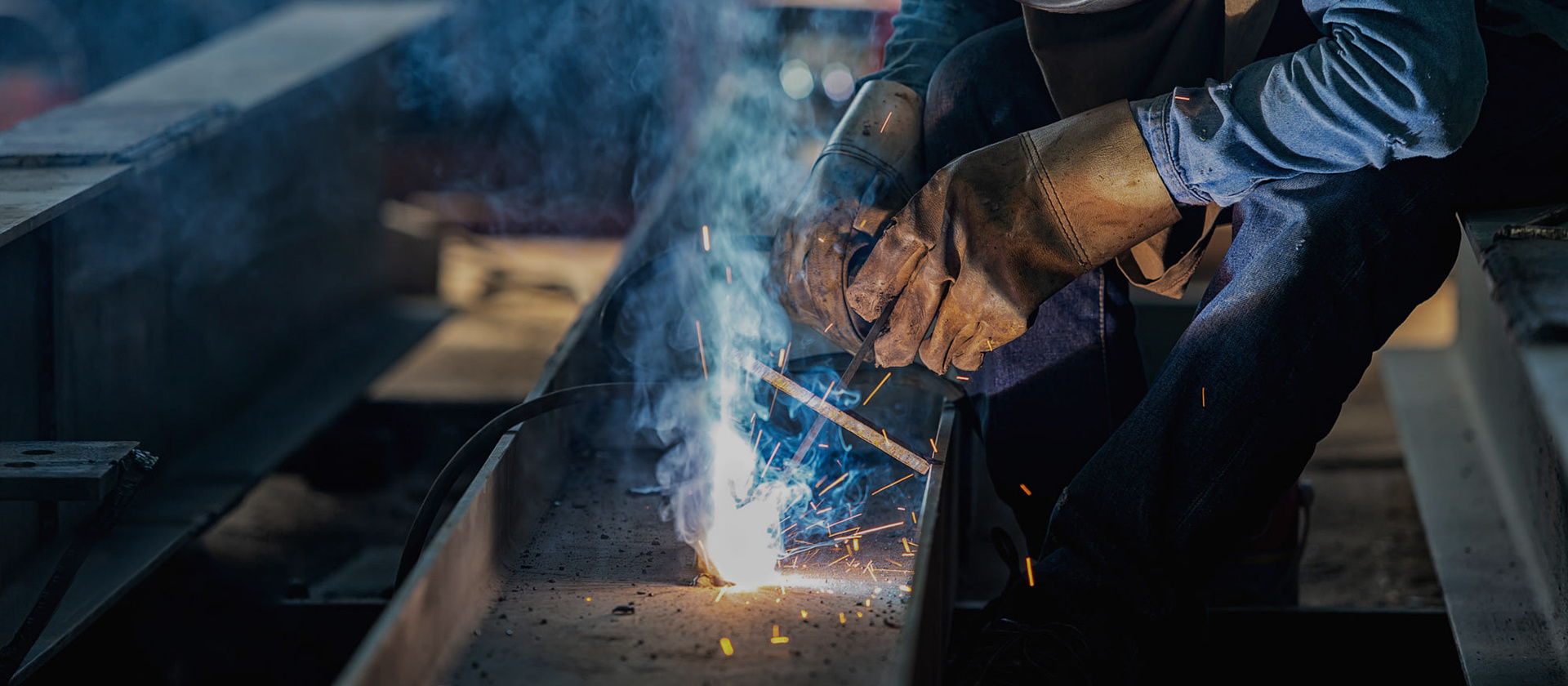
Introduction to Industrial Welding Techniques
Welding has become an indispensable process across various industries, serving as the backbone of manufacturing, construction, and repair. With increasing demands for durability and precision in industrial applications, understanding the intricacies of welding techniques is essential for professionals. This article delves into the art of welding, shedding light on methods, equipment, and safety practices that can enhance the quality of your work and meet the stringent requirements of modern industrial standards.
The Importance of Precision in Welding
Precision welding is critical not only for the structural integrity of the welded joints but also for overall project success. In industries such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery, even the slightest deviation can lead to catastrophic failures. Therefore, mastering precise welding techniques is paramount. This section explores why precision matters:
- **Quality Assurance**: Precision welding ensures that the finished product meets quality standards, reducing the risk of defects.
- **Cost Efficiency**: Accurate welding techniques minimize rework and waste, significantly lowering material and labor costs.
- **Safety**: Well-executed welds contribute to the safety of structures and machinery, preventing accidents that can arise from structural failures.
Overview of Popular Welding Methods
Various welding methods exist, each with unique advantages and applications. Understanding these methods allows professionals to select the most appropriate technique for their specific needs.
Arc Welding Techniques
Arc welding is one of the most widely used welding methods, primarily due to its versatility and effectiveness. It involves creating an electric arc between the electrode and the workpiece, generating sufficient heat to melt the metals and fuse them together. We will cover the following subtypes of arc welding:
- **Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)**: Often referred to as stick welding, SMAW is simple and cost-effective. It is suitable for outdoor use and can be performed on various metals.
- **Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)**: Also known as MIG welding, GMAW offers high deposition rates and is ideal for thin materials. It uses a continuous wire feed and an inert gas to protect the weld pool.
- **Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)**: Commonly known as TIG welding, this process is known for its precision and is used for thin metals and intricate welds.
MIG Welding: A Versatile Choice
MIG welding is favored for its ease of use and adaptability across various materials, such as aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel. The process involves feeding a continuous wire electrode through a welding gun, while an inert gas shields the molten weld pool from contamination. Key benefits include:
- **Speed**: MIG welding is faster than many other techniques, making it suitable for high-production environments.
- **Less Skill Required**: It is easier to learn, making it ideal for beginners and those transitioning into advanced welding applications.
TIG Welding: Achieving High Precision
TIG welding stands out for its ability to produce high-quality welds with excellent aesthetic appeal. It involves using a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a separate filler material, allowing for greater control and precision. TIG welding is often used in applications where visual quality and strength are crucial, such as in aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Spot Welding: Fast and Efficient
Spot welding is a process primarily used for joining sheet metal components. It involves applying pressure and heat to localized areas, creating welds at specific points. This technique is widely used in the automotive industry for assembling car bodies due to its speed and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Welding Technique for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate welding technique is vital in achieving optimal results. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- **Material Type**: Different materials require different welding techniques. For instance, aluminum may require TIG welding, while steel can often be effectively welded using MIG.
- **Thickness of Materials**: Thicker materials may require more robust techniques like SMAW, while thinner sheets can be handled with MIG or TIG.
- **Position of Welding**: The welding position (flat, horizontal, vertical, or overhead) can influence the choice of technique.
- **End Use**: For applications where aesthetics are important, such as in architecture, TIG welding might be the preferred choice due to its clean appearance.
Essential Welding Equipment and Components
To achieve precision in welding, having the right equipment is crucial. Here’s an overview of essential welding equipment:
- **Welding Machines**: The type of welding machine (MIG, TIG, or SMAW) will depend on the chosen welding technique. Ensure the machine is suitable for the materials and thickness you are working with.
- **Electrodes and Filler Rods**: Selecting the appropriate electrodes or filler rods is vital for ensuring compatibility with the base materials.
- **Protective Gear**: Safety gear, including helmets, gloves, and aprons, is essential for protecting the welder from harmful UV rays and sparks.
- **Clamps and Fixtures**: These tools help secure the workpieces in place, ensuring stability during the welding process.
Advanced Techniques for Enhanced Precision
For professionals looking to master welding, advanced techniques can significantly enhance precision and quality. Here are several methods worth exploring:
- **Pulse Welding**: This technique involves alternating between high and low current during welding, which can help control heat input and minimize distortion.
- **Laser Welding**: Utilizing concentrated laser beams, this method offers high precision and is ideal for thin materials and intricate designs.
- **Hybrid Welding**: Combining two welding processes, such as laser and MIG, allows for the benefits of both methods, improving efficiency and strength.
Safety Practices in Industrial Welding
Adhering to safety practices is critical in preventing accidents and injuries in welding environments. Essential safety tips include:
- **Proper Ventilation**: Ensure adequate ventilation to avoid the buildup of harmful fumes and gases.
- **Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Always wear appropriate gear, including a welding helmet with proper shade, gloves, and protective clothing.
- **Regular Equipment Maintenance**: Maintain welding equipment to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- **Fire Safety Precautions**: Keep flammable materials away from the welding area and have fire extinguishers readily available.
The Future of Welding Technologies
As technology continues to advance, the welding industry is likely to witness significant innovations. Automated and robotic welding systems are becoming increasingly popular, offering enhanced precision and efficiency. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning will further optimize welding processes, leading to improved quality and reduced costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best welding technique for beginners?
MIG welding is often recommended for beginners due to its ease of use and versatility.
2. How can I improve my welding precision?
Improving precision can be achieved through practice, the use of appropriate techniques, and maintaining your welding equipment.
3. What safety gear do I need for welding?
Essential safety gear includes a welding helmet, gloves, protective clothing, and appropriate footwear.
4. How do I choose the right welding machine?
Consider the materials you will be working with, the thickness of those materials, and the welding techniques you plan to use.
5. Are there any new technologies in welding?
Yes, advancements in automated and robotic welding systems, as well as the application of AI, are transforming the welding landscape.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Welding
Welding is a complex and vital skill in industrial applications, requiring a deep understanding of various techniques, equipment, and safety practices. By focusing on precision and continuously improving your skills, you can achieve high-quality results that meet the demands of today's industries. Embrace the art of welding, and unlock the potential for innovation and excellence in your projects.
Add
Xing village, lvgongbao town, renqiu city, hebei province, china